Overview
Osteoporosis is often called the “silent bone disease” because it progresses quietly over many years without obvious symptoms. By the time it is detected, bones may already be weak, leading to fractures from even minor falls or everyday movements. With longer life spans and sedentary habits, osteoporosis is becoming a major public health concern across the world.

In this article, we will understand osteoporosis in detail — what it is, why it happens, who is at risk, and how it can be prevented or managed.
What is Osteoporosis?
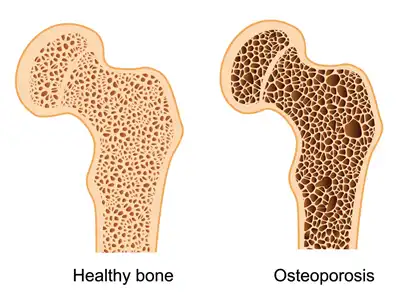
The word “osteoporosis” literally means “porous bones.” In healthy bones, there is a balance between bone formation by osteoblasts and bone resorption by osteoclasts. As we age, this balance can get disrupted, leading to decreased bone mineral density (BMD) and deterioration of bone microarchitecture.
This results in bones becoming:
- Thin and brittle
- Weak and fragile
- More prone to fractures, especially in the spine, hip, and wrist
Causes of Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis can result from multiple factors that either reduce bone formation or increase bone loss. The causes can be broadly divided into primary and secondary:
1. Primary Osteoporosis
- Postmenopausal osteoporosis: The most common type, caused by the sudden drop in estrogen levels after menopause. Estrogen plays a crucial role in maintaining bone density.
- Senile osteoporosis: Occurs in both men and women after the age of 70 due to aging, decreased calcium absorption, and reduced bone formation.
2. Secondary Osteoporosis
This occurs as a consequence of other conditions or medications, such as:
- Long-term corticosteroid therapy
- Endocrine disorders (hyperthyroidism, diabetes, Cushing’s syndrome)
- Malnutrition or eating disorders
- Gastrointestinal diseases causing poor calcium absorption (celiac disease, Crohn’s disease)
- Chronic kidney or liver disease
- Prolonged immobility or lack of exercise
Risk Factors of Osteoporosis
Not everyone develops osteoporosis, but some factors make it more likely:
- Non-modifiable risks
- Increasing age
- Female gender
- Family history of osteoporosis
- Asian and Caucasian ethnicity
- Modifiable risks
- Low dietary calcium and vitamin D
- Lack of exercise
- Smoking and alcohol use
- Being underweight or having eating disorders
- Poor nutrition in childhood or adolescence
Signs and Symptoms of Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis rarely causes pain or discomfort in its early stages. Many people do not realize they have it until a fracture occurs. Still, some warning signs can appear:
- Frequent fractures from minor injuries
- Back pain caused by collapsed vertebrae
- Loss of height over the years
- Stooped posture or rounded shoulders (kyphosis)
- Limited mobility in advanced cases
Common Sites of Osteoporotic Fractures
- Spine (vertebral compression fractures) – leading to height loss and kyphosis
- Hip fractures – associated with high morbidity and mortality in elderly patients
- Wrist fractures (Colles’ fracture) – often occur after minor falls
Diagnosis of Osteoporosis
Early detection is crucial to prevent complications. The following diagnostic tools are commonly used:
- Bone Mineral Density (BMD) Test
- The gold standard is DEXA scan (Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry).
- Provides a T-score:
- Normal: -1.0 and above
- Osteopenia: -1.0 to -2.5
- Osteoporosis: -2.5 and below
- X-rays
- May show fractures or bone thinning, but are less sensitive in the early stages.
- Laboratory Tests
- To rule out secondary causes: calcium, vitamin D, thyroid function tests, and kidney and liver function tests.
- FRAX Tool
- An online calculator used to estimate the 10-year fracture risk based on age, gender, family history, and lifestyle factors.
Management and Treatment of Osteoporosis
The goal of treatment is to strengthen bones, prevent fractures, and maintain independence. Management includes lifestyle changes, nutrition, and in some cases, medicines.
Lifestyle Measures
- Regular exercise: Walking, jogging, weight training, and yoga strengthen bones and improve balance.
- Fall prevention: Use anti-slip footwear, keep the home well-lit, and avoid clutter that may cause tripping.
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol.
Nutrition
- Calcium: Aim for 1000–1200 mg daily through milk, curd, cheese, sesame seeds, almonds, and leafy greens.
- Vitamin D: Sunlight exposure plus foods like fortified milk, egg yolk, and supplements if required.
- Protein and minerals: Adequate protein, magnesium, and phosphorus are also important.
Prevention of Osteoporosis
Since bone loss starts silently, preventive steps from a young age are vital.
- In children and teens: Encourage outdoor play, a calcium-rich diet, and an active lifestyle.
- In adults: Maintain a healthy body weight, stay physically active, and avoid smoking.
- In elderly and postmenopausal women: Regular bone check-ups, supplementation if needed, and fall-prevention strategies.
Complications of Osteoporosis
If not addressed, osteoporosis can lead to:
- Multiple fractures and deformities
- Reduced independence and mobility
- Emotional issues like depression and anxiety
- Increased risk of death after hip fractures, especially in older adults
Conventional vs. Homoeopathic Approach
Conventional medicine mainly relies on calcium supplements, vitamin D, bisphosphonates, and hormone therapy to slow down bone loss. While these help in controlling progression, they often bring side effects and don’t address the individual constitution of the patient.
Homoeopathy, on the other hand, is based on the principle of “like cures like.” Remedies are chosen after studying the patient’s physical complaints, emotional state, lifestyle, and family history. The aim is not only to strengthen bones but also to correct the underlying imbalance that makes a person prone to osteoporosis.
Homoeopathic Remedies for Osteoporosis
There is no single “medicine” for osteoporosis in homeopathy. Remedies are selected according to the patient’s constitution, symptoms, and modalities. Some commonly used remedies include:
- Calcarea Carbonica
- Suited for overweight, chilly individuals with weak digestion.
- Useful when bones are weak and fractures heal slowly.
- Often indicated in women with early menopause or hormonal imbalance.
- Calcarea Phosphorica
- Good for thin, delicate, and weak constitutions.
- Helpful in delayed bone healing after fractures.
- Especially useful in children, teenagers, and elderly people with weak bones.
- Silicea
- For patients with fragile bones and frequent suppurations.
- Helps in the slow healing of fractures.
- Suited to nervous, delicate individuals who catch a cold easily.
- Phosphorus
- Suited for tall, thin individuals with a nervous, sensitive temperament.
- Useful in cases of osteoporosis with frequent spinal or hip issues.
- Symphytum Officinale (Comfrey)
- Known as the “bone knitting remedy.”
- Very effective in accelerating fracture healing and reducing pain.
- Often used as a supportive remedy along with constitutional medicines.
- Ruta Graveolens
- Helpful when osteoporosis leads to bone pain and weakness of tendons/ligaments.
- Also used for joint pains associated with bone weakness.
Note: Homoeopathic remedies should not be self-prescribed. A qualified homeopathic physician should select medicines after detailed case-taking.
Why choose Dr. Sanjay’s Homoeopathy for Osteoporosis treatment in Lucknow, India?
Dr. Sanjay’s Homoeopathy is a trusted clinic for safe and effective Osteoporosis treatment in Lucknow, India. With years of expertise, Dr. Sanjay is one of the best Osteoporosis treatment doctors in Lucknow, India. He offers specialized homeopathic treatment that helps manage weak bones, frequent fractures, back pain, and reduced mobility naturally, without side effects. As a leading homeopathic doctor in Lucknow, he follows international treatment standards and offers personalized care that focuses on strengthening bones, improving calcium absorption, and enhancing overall bone density. Patients choose Dr. Sanjay’s Homoeopathy for its holistic healing, long-lasting relief, and compassionate approach in managing chronic bone conditions like Osteoporosis.


