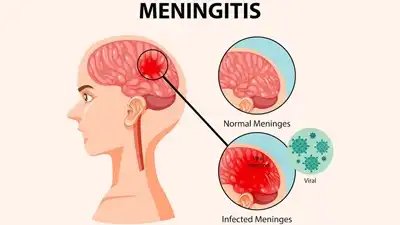
What is Meningitis?
Meningitis is the inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. It occurs when these layers become infected or irritated due to bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other causes. The inflammation can lead to swelling, increased pressure in the brain, and disrupted nerve function.

Depending on the cause, meningitis can be mild or life-threatening. Early recognition is important to prevent complications. Symptoms often include headache, fever, and neck stiffness. Meningitis can affect people of all ages, but infants, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals are at higher risk.
What are the symptoms of Meningitis?
Meningitis symptoms usually appear suddenly. Common signs include severe headache, fever, stiff neck, nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light, and confusion. In infants, symptoms may also include irritability, poor feeding, unusual crying, and a bulging soft spot on the head. Fatigue, drowsiness, or difficulty waking may occur in severe cases. Skin rashes, especially purplish spots, can indicate bacterial meningitis. Some symptoms overlap with other illnesses, making early medical assessment crucial. Rapid diagnosis and treatment are essential, as bacterial meningitis can progress quickly and lead to serious complications if left untreated.
What causes Meningitis?
Meningitis can be caused by bacterial, viral, or fungal infections, each affecting the meninges differently. Bacterial meningitis is severe and requires urgent treatment. Viral meningitis is more common but usually less dangerous. Fungal meningitis is rare and mostly affects those with weakened immune systems. Non-infectious causes include injury, certain medications, autoimmune conditions, and cancers that irritate the meninges. The infection often spreads through respiratory droplets or the bloodstream, depending on the type. Environmental and lifestyle factors, such as close living conditions and poor hygiene, can also increase the risk of contracting infectious meningitis.
How is Meningitis spread?
Meningitis spreads primarily through close contact with infected respiratory or throat secretions. Bacterial strains, such as meningococcal bacteria, are transmitted by coughing, sneezing, kissing, or sharing utensils. Viral meningitis can spread through fecal-oral contact, contaminated surfaces, or respiratory droplets. It is less commonly spread through blood or other bodily fluids. Non-infectious meningitis cannot be transmitted. Risk is higher in crowded living environments, daycare centers, and schools. Proper hygiene, avoiding sharing personal items, and vaccinations reduce the risk. Early treatment of infected individuals also prevents further spread of the disease.
Is Meningitis contagious?
Some types of meningitis are contagious, particularly bacterial and viral forms. Bacteria like Neisseria meningitidis can spread through close contact, such as coughing, sneezing, or kissing. Viral meningitis often spreads through respiratory secretions or contaminated surfaces. Fungal meningitis and meningitis caused by injury or medications are not contagious. Contagious forms are more likely in crowded places, schools, or dormitories. Early identification and isolation of infected individuals can reduce transmission. Vaccination against certain strains, such as meningococcal bacteria, also helps prevent outbreaks and protects communities from highly contagious meningitis types.
How is Meningitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis starts with a physical examination and assessing symptoms like fever, headache, and neck stiffness. A lumbar puncture (spinal tap) is the most definitive test, where cerebrospinal fluid is analyzed for infection, white blood cells, and protein levels. Blood tests can detect bacteria or viruses in the bloodstream. Imaging like CT or MRI scans, may help identify swelling or complications in the brain. In some cases, throat swabs or urine tests are done to detect the specific pathogen. Accurate diagnosis ensures timely treatment and reduces the risk of severe complications or death.
Can Meningitis be cured?
Yes, meningitis can often be cured, especially with prompt and appropriate treatment. Bacterial meningitis requires immediate antibiotics, and most patients recover fully if treated early. Viral meningitis usually resolves on its own with supportive care. Fungal meningitis can be treated with antifungal medications, though recovery may be slower. Delayed treatment increases the risk of serious complications like brain damage, hearing loss, or death. Prevention through vaccination and hygiene is important. Early medical attention at the first sign of symptoms is the key to successful treatment and full recovery in most cases.
Can Meningitis be prevented?
Yes, meningitis can be prevented through vaccination, hygiene, and healthy practices. Vaccines protect against bacterial types like meningococcal, pneumococcal, and Hib. Washing hands regularly, avoiding sharing utensils, and covering the mouth when sneezing or coughing reduce the spread. People in high-risk environments, such as schools, dormitories, or healthcare settings, should take extra precautions. Prompt treatment of respiratory infections also reduces the risk. While not all types of meningitis can be prevented, vaccines and good hygiene significantly reduce the chances of contracting the most dangerous forms.
Who is at risk for Meningitis?
Meningitis can affect anyone, but certain groups are at higher risk. Infants and young children, adolescents, the elderly, and people with weakened immune systems are more vulnerable. Individuals living in crowded settings, such as dormitories or military barracks, are at increased risk. Travelers to regions with meningitis outbreaks, those with chronic illnesses, or people without prior vaccination are also more susceptible. Early recognition and preventive measures, such as vaccination and hygiene, are crucial for these high-risk groups to avoid infection and complications.
What foods or home remedies can help with Meningitis recovery?
Recovery from meningitis primarily depends on medical treatment. Supportive care can include hydration, rest, and a nutritious diet. Soft, easily digestible foods rich in vitamins, minerals, and protein help repair tissues and strengthen immunity. Hydrating fluids like water, soups, and herbal teas aid recovery. Avoid alcohol, processed foods, or heavy meals that stress the body. Gentle physical activity after acute recovery improves energy and circulation. Home remedies cannot replace medical care but can support overall health. Monitoring for lingering symptoms and following the doctor’s advice is crucial for complete recovery.
Homeopathic Approach to Meningitis Treatment
General Principles
- Homeopathy focuses on stimulating the body’s natural defense mechanisms rather than directly targeting the pathogen.
- In acute conditions like meningitis, immediate medical attention is critical; homeopathy can be used alongside conventional care for supportive treatment, but it cannot replace urgent hospitalization, especially in bacterial meningitis.
- The remedy is chosen based on the totality of symptoms, including fever pattern, mental state, neurological signs, and physical manifestations.
Commonly Considered Homeopathic Remedies
Remedies must be prescribed by a qualified homeopath based on individual symptoms.
- Belladonna – Sudden onset of high fever, red face, throbbing headache, sensitivity to light, restlessness.
- Gelsemium – Weakness, drowsiness, heaviness of head and eyelids, trembling, slow onset of symptoms.
- Rhus Toxicodendron – Stiff neck, pain in back and muscles, aggravation on initial movement.
- Apis Mellifica – Swelling, burning or stinging pain, and heat in the head.
- Aconitum Napellus – Early stage after sudden exposure, fear, restlessness, anxiety, and dry skin.
- Helleborus Niger – Confusion, drowsiness, and delirium in severe cases.
Note: Acute bacterial meningitis is life-threatening; homeopathic remedies are supportive but should not delay antibiotics or hospitalization.
Supportive Measures in Homeopathy
- Rest and a quiet environment to reduce stress on the nervous system.
- Hydration to support overall body function.
- Monitoring of fever, mental state, and neurological signs.
- Follow up with homeopathy for the recovery phase to restore immunity and prevent complications like post-infection fatigue, headaches, or lingering neurological effects.
Why choose Dr. Sanjay’s Homoeopathy for Meningitis treatment in Lucknow, India?
Dr. Sanjay’s Homoeopathy is a trusted clinic for safe and effective Meningitis treatment in Lucknow, India. With years of expertise, Dr. Sanjay is the best Meningitis treatment doctor in Lucknow, India, and provides specialized homeopathy treatment that helps manage fever, severe headaches, neck stiffness, sensitivity to light, and other neurological symptoms naturally without side effects. As a leading homeopathic doctor in Lucknow, he follows international treatment standards and offers personalized care that addresses the root cause of Meningitis while strengthening immunity and supporting nervous system health. Patients choose Dr. Sanjay’s Homoeopathy for its holistic healing, long-lasting relief, and compassionate approach in managing serious infections like Meningitis.


